Color is often one of the first things we notice when looking at an object. It can affect how we perceive and communicate.
But it is often difficult to describe. How do you define blue other than to call it blue? There are quite a few words that help define color and how different colors work together and how they are used in the design process.
Understanding the lingo is important when clients and designers are working together so that there is a mutual understanding, making projects come together more effectively and efficiently.
Here is a glossary containing the most common words and phrase used to define and describe color.
Achromatic Color
Colors that are “colorless†such as white, black or gray are achromatic; these are also called “hueless.†These colors are considered neutrals and can be combined with any other color.
Additive Color
Mixing two or more colors creates additive color. Primary colors red, blue and yellow are the starting point for additive color mixing because they are used to create every color in the visible spectrum. This is a method of digital color mixing in which colors are added to bring the hue closer to white.
Analogous Colors
Colors that are located in adjacent locations on the color wheel are called analogous colors. They can be put together to create almost monochromatic color schemes.
Brightness
Brightness relates to the intensity of light coming from an image or color. The more light it looks like a color emits, the more brightness it has. A brightness scale is often used in the image editing process to enhance parts of images.
Chroma
A color’s purity is described as chroma or chromaticity. The purest hues (with the highest chroma) are those which do not have the addition of white or black in them. Colors with high chroma are especially vivid and often have a high brightness. The terms chroma and saturation are often interchanged, although they have different meanings.
CMYK
CMYK is a color system used in printing, referring to the colors of ink used in the printing process – cyan, magenta, yellow and black. CMYK color is also called process color.
Color Match
Color match occurs when two hues appear to be identical even if they are not composed identically. This term is often used in commercial applications when an exact color is unknown and needs to be replicated.
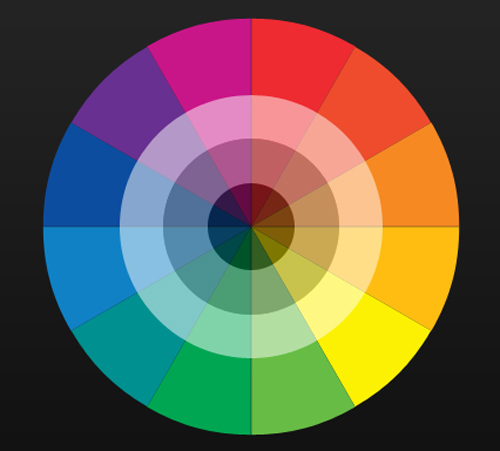
Color Wheel (or Circle)
The color wheel is one of the oldest methods of categorizing color that is still used today. The wheel arranges colors visually according to relationship by chroma. You can use the wheel, or circle, to pair colors and create color palettes.
Complementary Colors
Colors located at opposite locations on the color wheel are complementary. Primary colors can never complement each other. Red and green or blue and orange, for example, are pairs of complementary colors. Complementary colors often have high contrast with each other when paired.
Cool, or Passive, Colors
Cool colors are those that often carry some visual weight and are thought to be darker than active or warm colors. They tend to recede from images as well. Colors in the active range on the color wheel are blue-violet to blue to green to yellow-green.
Gamut
All of the possible colors in a color system are referred to as a gamut. No single system can reproduce every color in the spectrum, you would need multiple gamuts to achieve this. Gamuts can include overlapping colors.
Gray Scale
An achromatic color scale that includes only grays and no other hues. Images without color are often referred to as “black and white†or “gray scale.â€
Hue
The identifier of color as it relates to the color name, such as red, blue, yellow, green or purple. Black, white and gray do not contain a hue.
Hex Values
CMYK is a color system used to define colors on web pages. Colors are named using a system of three pairs of numbers, the first two digits represent red, the second pair green and third pair blue. Hex values can contain both letters and numbers, in the format #000000 (black) or #ffffff (white) or #00ff00 (green).
Matte
Any color that seems flat or contains no luster, gloss or reflective properties is called matte.
Primary Colors
The three basic colors that make up every color are called primary colors. They are red, blue and yellow.
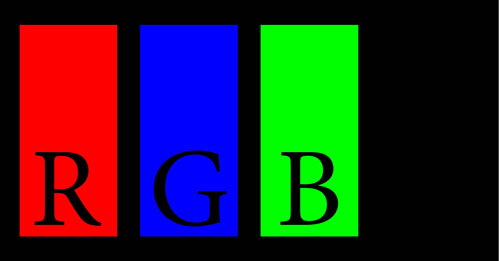
RGB
RGB is a color system used in digital media. On screens red, green and blue light are used to create every color you see. Mixing all three at a top intensity creates white, mixing all three with no intensity creates black. All other colors are created with values in between.
Saturation
Technically, saturation refers to how a color appears in certain lighting conditions. But more it is used interchangeably with chroma, to refer to how pure a color is. Gray, for example, has zero saturation and adding it to a color lessens the saturation of that hue.
Secondary Colors
Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors. They are orange (red and yellow), green (yellow and blue) and purple or violet (blue and red).
Shade
Any addition of black to a color to make it darker is called a shade.
Subtractive Color
The physical mixing of colors to bring each hue closer to black is called subtractive color mixing. This theory is used most commonly by artists when mixing paints.
Tertiary Colors
Mixing a primary and secondary color results in tertiary colors. There are six such hues – yellow-green, yellow-orange, red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet and blue-green.
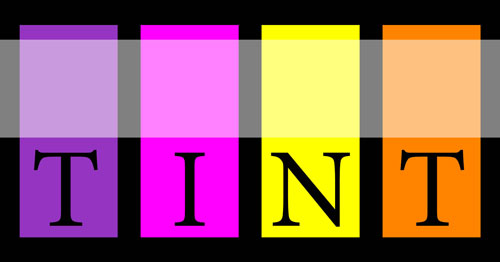
Tint
Any addition of white to a color to make it lighter is called a tint.
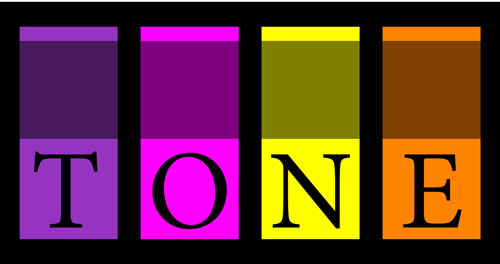
Tone
Any addition of gray to a color to make it less intense is called a tone.
Warm, or Active, Colors
Warm colors are those that do not have a lot of visual weight and appear to encourage activity or movement. The colors are often lighter and used with increased brightness. Colors in the active range on the color wheel are red-violet to red to yellow to yellow-green.